GLP-1 Agonists Uncovered: Comparing Tirzepatide, Semaglutide, and Liraglutide
In the burgeoning field of weight management, the new class of medications called GLP-1 receptor agonists has made a remarkable entrance. Medications such as semaglutide, liraglutide, and tirzepatide are altering the landscape of weight loss and health management. However, each has distinct characteristics and potential applications. Let's delve into these medications and understand their differences.
What is a GLP-1 receptor agonist?
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of medications initially designed to manage Type 2 diabetes. Recently, they have received attention in the field of weight management for their appetite-suppressing properties. They function by mimicking the activities of the body's natural GLP-1 hormone, which decreases appetite and manages blood sugar levels.
For a deep (really deep) dive into the research studies that show the mechanics and efficacy of GLP-1 medications for weight loss, this video from Harvard Medical School gives in depth answers.
Semaglutide in Focus
Semaglutide, marketed under the brand name Ozempic for diabetes and Wegovy for weight loss, is a once-weekly injectable medication already approved by the FDA for weight management. Clinical trials showed an average weight loss of about 15% of body weight over a year. However, it's important to note that semaglutide might not be suitable for people with a history of thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
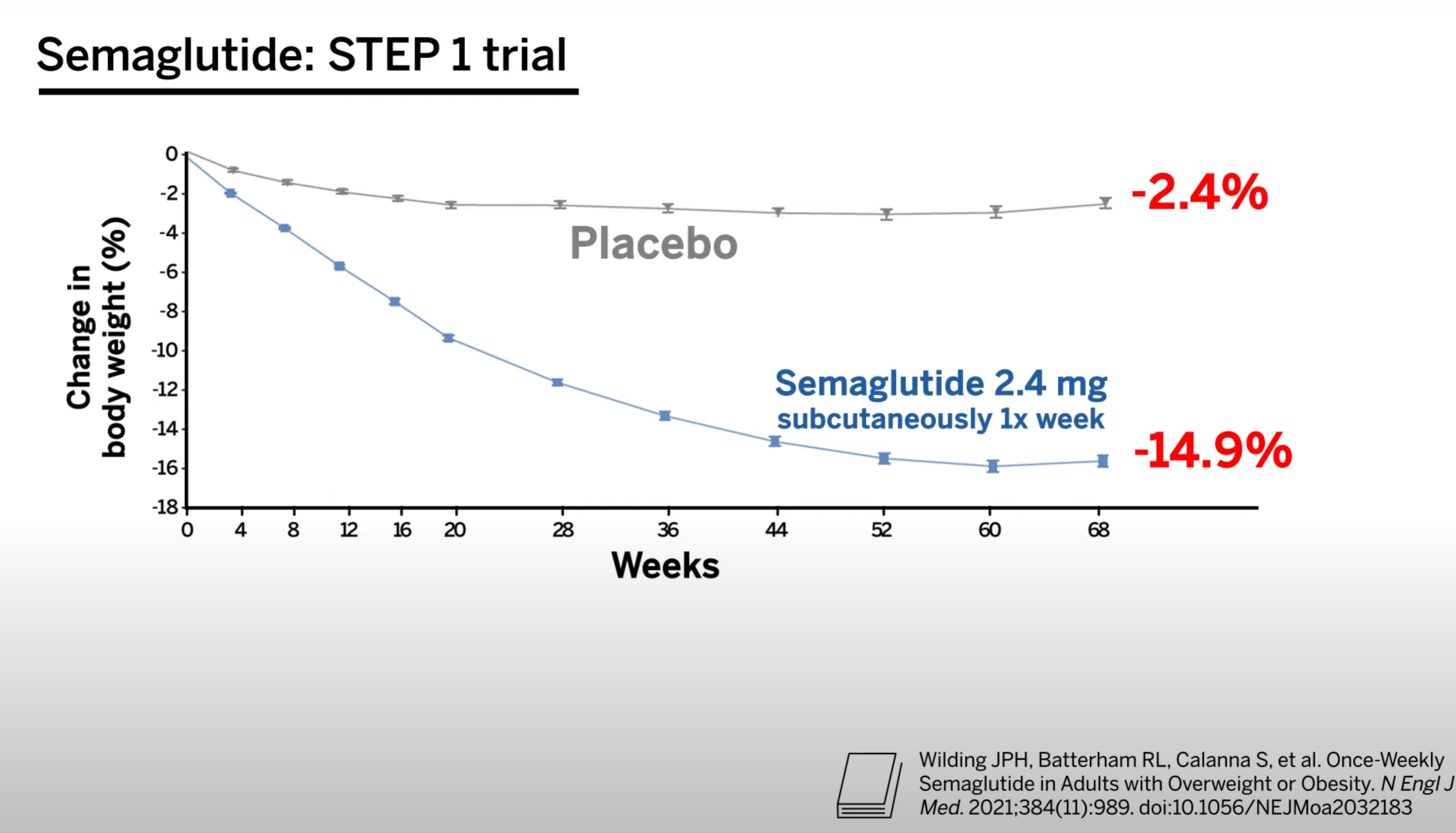
Exploring Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is unique among GLP-1 receptor agonists because it also incorporates GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) action. GIP is another hormone that plays a role in managing blood sugar levels and appetite. This dual action makes tirzepatide a particularly exciting candidate for weight management. In clinical trials, patients using tirzepatide reported an average weight loss of up to 20% of their body weight over a year. However, while approved by the FDA for Type 2 diabetes under the brand name Mounjaro, tirzepatide is still in the late stages of the approval process for weight loss.
The Role of Liraglutide
Liraglutide, commercialized under the brand name Saxenda, is a daily injectable treatment. It has been in use for weight management for several years, with patients typically experiencing around a 5-10% body weight loss. Like semaglutide, liraglutide is contraindicated in individuals with a history of thyroid cancer or MEN 2.
Head to Head Comparison
While all three medications operate on the same principle, there are differences between them. Tirzepatide, with its dual GLP-1 and GIP action, seems to show the highest weight loss potential, though it is still under evaluation. Semaglutide, with its FDA approval and strong clinical trial results, offers a proven path for weight loss. Liraglutide has a longer track record and more long-term data on outcomes, though it requires a daily injection.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing between these options should involve a discussion with your healthcare provider, considering your individual health circumstances, weight loss goals, and the potential side effects. Remember, these medications are not miracle cures but tools that work best when combined with lifestyle changes like a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Conclusion
The development of GLP-1 agonists like tirzepatide, semaglutide, and liraglutide represent a significant shift in our approach to weight management. As research continues to evolve, so too will our understanding of these potent tools for optimal health and weight management.



